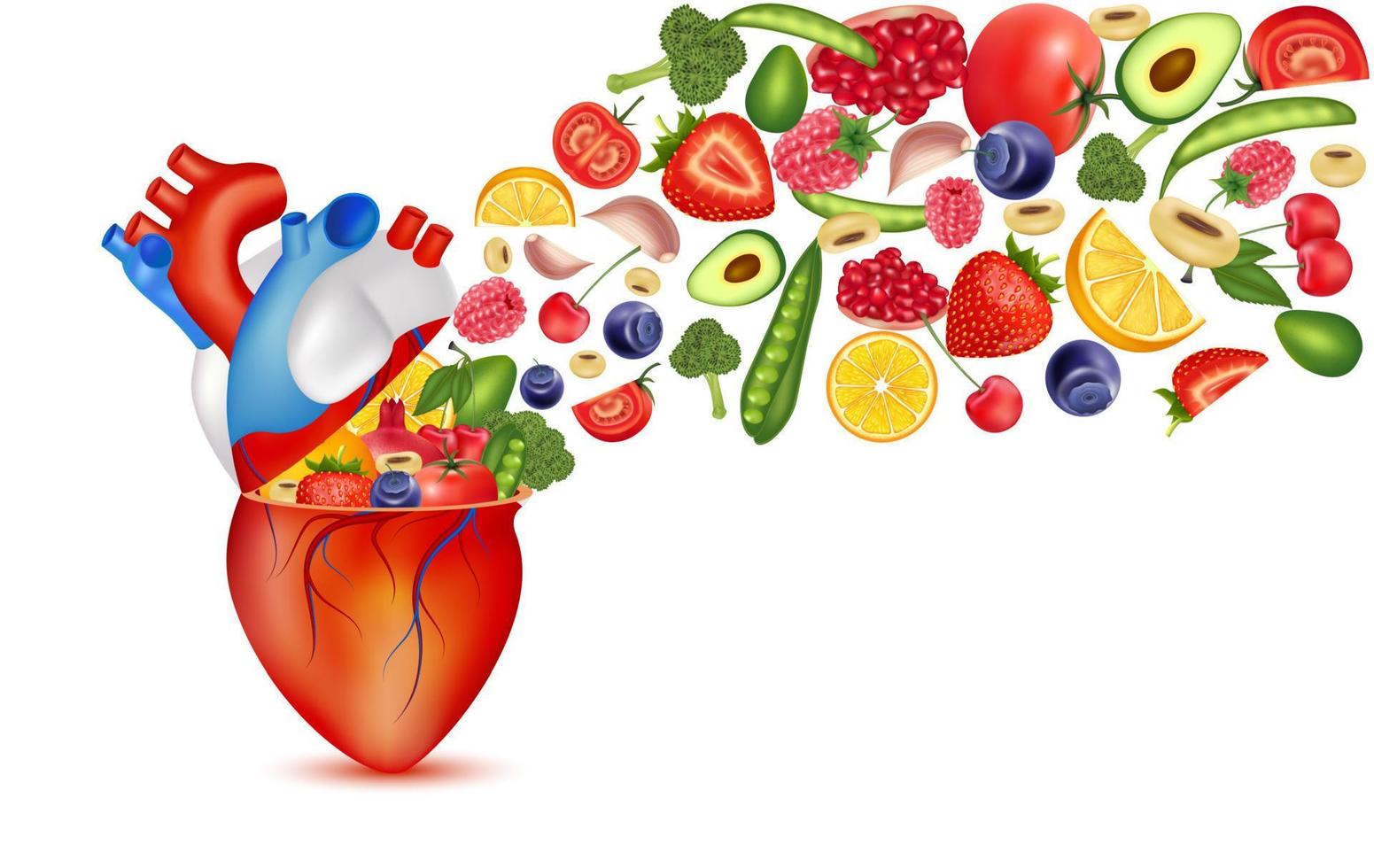
In recent years, plant-based diets have gained significant attention for their potential health benefits. Adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds can be transformative for overall health. This article explores the key health benefits of a plant-based diet, backed by research and expert insights.
Improved Cardiovascular Health
One of the most celebrated benefits of a plant-based diet is its positive impact on cardiovascular health. Research shows that plant-based diets are associated with lower risks of heart disease, hypertension, and stroke. Key factors include:
- Lower Cholesterol Levels: Plant-based diets are typically low in saturated fats and cholesterol, which helps reduce blood cholesterol levels.
- Reduced Blood Pressure: Consuming foods high in potassium, magnesium, and fiber—common in plant based diets—can help lower blood pressure.
- Enhanced Blood Vessel Function: Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in plant based foods support healthier blood vessels.
Weight Management and Obesity Prevention
A plant-based diet can be an effective strategy for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing obesity. Key benefits include:
- Lower Caloric Density: Plant-based foods are generally lower in calories and higher in nutrients compared to animal products, which can help with weight management.
- High Fiber Content: Fiber-rich foods promote satiety and reduce overall calorie intake, aiding in weight loss and weight maintenance.
- Balanced Metabolism: Nutrient-dense plant foods support a healthy metabolism and energy balance.
Enhanced Digestive Health
The high fiber content of a plant-based diet is beneficial for digestive health. Benefits include:
- Improved Bowel Regularity: Fiber helps regulate bowel movements and prevents constipation.
- Gut Health Support: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for overall digestive health.
- Reduced Risk of Digestive Disorders: High-fiber diets are linked to a lower risk of conditions such as colorectal cancer and diverticulitis.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Plant-based diets are associated with a lower risk of several chronic diseases, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Plant based eating patterns can improve insulin sensitivity and help manage blood sugar levels.
- Certain Cancers: Antioxidants and phytochemicals in plant foods may reduce the risk of certain cancers, including breast, prostate, and colon cancer.
- Kidney Disease: Lower protein intake from animal sources may benefit kidney function and reduce the risk of chronic kidney disease.
Improved Mental Health and Cognitive Function
Emerging research suggests that plant-based diets may also positively impact mental health and cognitive function:
- Mood Enhancement: Nutrient-rich plant foods can influence brain chemistry and improve mood. For instance, omega-3 fatty acids from flaxseeds and walnuts support mental well-being.
- Cognitive Benefits: Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds found in plant based foods may protect against cognitive decline and support brain health.
Sustainable and Ethical Considerations
Beyond personal health benefits, a plant-based diet has broader implications for sustainability and ethics:
- Environmental Impact: Plant based diets have a lower carbon footprint and are less resource-intensive compared to diets high in animal products.
- Ethical Concerns: Reducing animal product consumption aligns with ethical considerations regarding animal welfare and factory farming practices.
Tips for Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
If you’re considering transitioning to a plant based diet, here are some practical tips:
- Start Gradually: Begin by incorporating more plant-based meals into your diet and gradually reducing animal products.
- Focus on Variety: Ensure your diet includes a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds to meet your nutritional needs.
- Read Labels: Pay attention to food labels to avoid hidden animal products and ensure you’re getting sufficient nutrients.